Ball of Foot Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Relief
Have you ever experienced a sudden, sharp pain in the ball of your foot? If so, you’re not alone. Ball of foot pain is a common complaint, and understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help you find relief and prevent future discomfort. In this blog post, we will delve into the anatomy of the foot, discuss common conditions causing ball of foot pain, and provide tips for prevention and treatment.
Short Summary
- Ball of foot pain, or metatarsalgia, is caused by a loss of the fat pad in the ball of the foot and excessive pressure on it.
- Common conditions that can cause ball of foot pain include metatarsalgia, Morton’s neuroma and sesamoiditis.
- Preventative measures such as choosing appropriate footwear and maintaining a healthy body weight can help reduce risk. Diagnosis includes physical examination with potential imaging tests while treatments range from home remedies to medical interventions & surgical options.
Understanding Ball of Foot Pain
Ball of foot pain, also known as metatarsalgia, can manifest as:
- Shooting pain in the affected area
- Swelling
- Painful calluses
- Burning pain
This discomfort is typically caused by a loss of the fat pad underneath the ball of the foot  and excessive pressure on the area, which can be exacerbated by excess weight.
and excessive pressure on the area, which can be exacerbated by excess weight.
To understand the causes and treatment options for ball of foot pain, it’s essential to grasp the anatomy of the foot and the factors that contribute to this discomfort.
Anatomy of the Foot
The foot is a complex structure consisting of 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments that play a crucial role in body weight transfers during movement. The metatarsals, five long bones in the forefoot that connect the ankle to the toes, are particularly important when discussing ball of foot pain.
The ball of the foot is the region located at the base of the toes, where the metatarsals and phalanges intersect, also referred to as the metatarsal-phalangeal joint. During certain activities, this joint, especially near the second toe, can be subjected to extra pressure, leading to discomfort and pain.
Causes of Pain
There are several frequent causes of pain in the ball of the foot, such as:
- Excessive pressure
- Ill-fitting footwear
- Preexisting medical conditions like stress fractures
- Metatarsalgia, a condition characterized by metatarsal pain
Foot deformities, such as bunions, can also contribute to ball of foot pain. A bony bump develops on the joint at the base of the big toe; this is known as a bunion. It can push the big toe inwards towards the other toe bones and cause the ball of the foot to widen. Patients with bunions may experience redness, swelling, stiffness, difficulty moving the big toe, and aching pain in the ball of the foot. Wearing properly fitted shoes with a wider toe box is one treatment option for bunions. Orthotics and other devices can also reduce pressure on the affected area and correct toe position. Additionally, exercises to strengthen and stretch the foot muscles should be performed and over-the-counter pain medication can be taken to alleviate ball of foot pain.
Potential risk factors for metatarsalgia include high-impact activities, foot deformities, and wearing high heels. By understanding these causes and risk factors, we can take steps to prevent and treat pain in the ball of the foot.
Common Conditions Causing Ball of Foot Pain
Several conditions are frequently associated with ball of foot pain, including metatarsalgia, Morton’s neuroma, and sesamoiditis, which often affects the metatarsal heads. Knowing the details of these conditions and their symptoms can help you identify the cause of your discomfort and seek appropriate treatment.
Let’s explore each of these conditions in more detail.
Metatarsalgia
Metatarsalgia is a condition characterized by:
- Pain and inflammation in the metatarsals, the long bones located in the anterior
 of the feet, just below the toes
of the feet, just below the toes - Discomfort in the metatarsal region beneath the ball of the foot, which may or may not be accompanied by contusions and swelling or inflammation
- Symptoms that can manifest rapidly or gradually
- Causes such as high-impact sports with frequent running and jumping, extended walking, wearing high heels or snug-fitting shoes, foot deformities, and various medical conditions
Individuals who participate in high-impact sports, those with high arches, and those with foot deformities such as hammertoes and bunions, are more likely to experience metatarsalgia. Treatment for metatarsalgia may include the use of a metatarsal pad, a surgical shoe, or a shoe insert to reduce pressure on the affected area of the foot. In cases where more aggressive treatment is required, an injection or surgery may be necessary. Additionally, ice and rest are recommended treatments for metatarsalgia at home.
If left unaddressed, metatarsalgia can result in hammertoes, limping, and pain in other parts of the body, such as the lower back and hip, due to altered gait patterns. More information on Metatarsalgia.
Morton’s Neuroma
Morton’s neuroma is a condition characterized by pain and inflammation in the ball of the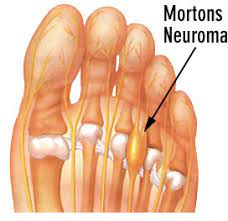 foot, caused by the thickening of the tissue around a nerve. This condition is typically caused by compression of a nerve in the ball of the foot and can be attributed to wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes, or due to an injury or trauma to the foot. The most prevalent indication of Morton’s neuroma is a sharp, burning sensation in the ball of the foot that may extend into the toes, along with tingling, numbness, and a feeling of having a pebble in the shoe.
foot, caused by the thickening of the tissue around a nerve. This condition is typically caused by compression of a nerve in the ball of the foot and can be attributed to wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes, or due to an injury or trauma to the foot. The most prevalent indication of Morton’s neuroma is a sharp, burning sensation in the ball of the foot that may extend into the toes, along with tingling, numbness, and a feeling of having a pebble in the shoe.
Treatment options for Morton’s neuroma may include steroid injections, orthotics, and surgery to remove or reposition some of the nerve or tissue in the foot. By identifying the cause of Morton’s neuroma and seeking appropriate treatment, you can alleviate the discomfort associated with this condition.
Sesamoiditis
Sesamoiditis is an inflammatory condition that affects the sesamoid bones. It can be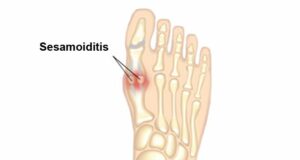 caused by overuse, repetitive stress or a direct injury. Symptoms of sesamoiditis may include tenderness and pain in the ball of the foot, along with swelling. Flexing or extending the big toe may be challenging, making it difficult to walk and bear weight on the affected foot.
caused by overuse, repetitive stress or a direct injury. Symptoms of sesamoiditis may include tenderness and pain in the ball of the foot, along with swelling. Flexing or extending the big toe may be challenging, making it difficult to walk and bear weight on the affected foot.
Resting can help reduce ball of foot pain and inflammation associated with sesamoiditis. Additionally, icing the affected area and taking anti-inflammatory medication can offer further relief. Taping, padding or orthotics may be used to provide support for the affected area. This can help reduce pressure and promote healing.
In certain cases, sesamoid bones require immobilization for proper healing. This can be accomplished through the use of a cast or specialized walking boot.
Preventing Ball of Foot Pain
Preventing ball of foot pain is possible by implementing a few simple strategies, such as choosing proper footwear, using arch supports and metatarsal pads, and maintaining a healthy body weight.
By taking these preventative measures, you can reduce the risk of developing pain in the ball of the foot and promote overall foot health.
Choosing Proper Footwear

Selecting the right shoes is crucial for preventing ball of foot pain. Appropriate footwear, such as shoes with shock-absorbing insoles or arch supports, can help avert or reduce potential issues with metatarsalgia. When choosing shoes, it’s essential to ensure that they fit properly and that there is a half inch of space between the toe and the tip of the shoe.
By wearing comfortable shoes that provide adequate support, you can reduce the strain on the ball of the foot and alleviate discomfort. Wearing shoes that are suitable for your activities is particularly important for individuals who participate in high-impact sports or have foot deformities.
Arch Supports and Metatarsal Pads
Arch supports, also known as orthotics, can play a significant role in alleviating and preventing ball of foot pain. They provide support to the arches of the feet, evenly distribute pressure, and optimize alignment, thus providing relief from foot pain and discomfort.
Similarly, metatarsal pads can cushion and support the metatarsal bones in the ball of the foot, providing relief from pain and discomfort as well as helping to prevent further pain and discomfort. When selecting arch supports and metatarsal pads, it’s crucial to ensure they fit correctly, offer adequate support, and are made of a long-lasting material.
Maintaining a Healthy Body Weight
Maintaining a healthy body weight is of great importance for overall health and wellbeing. Being overweight or obese can heighten the risk of developing various health conditions, including:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Type 2 diabetes
- Certain types of cancer
Furthermore, sustaining a healthy body weight can assist in decreasing the pressure on the ball of the foot, thus potentially reducing pain.
To maintain a healthy body weight, focus on eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, getting adequate sleep, and managing stress. Additionally, reduce consumption of sugary drinks, processed foods, and foods high in saturated fat.
Diagnosing and Treating Ball of Foot Pain
Diagnosing and treating ball of foot pain involves a combination of home remedies, medical interventions, and, in some cases, surgical options. By understanding the diagnosis process and exploring various treatment options, you can find relief from ball of foot pain and return to an active lifestyle.
The first step in diagnosing ball of foot pain is to identify the underlying cause. Common causes are common causes.
Diagnosis Process
If you’re experiencing ball of foot pain, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a general practitioner or a podiatrist, to evaluate your symptoms and determine the underlying cause. The diagnosis process typically involves:
- A physical examination of the foot
- A discussion about the history of the pain and any activities that could have caused the discomfort
- In some cases, imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans, may be necessary to rule out other conditions.
Once the cause of your pain has been identified, your healthcare provider can recommend appropriate treatment options to help alleviate your discomfort and improve your overall foot health.
Home Remedies
There are several home remedies that can help alleviate ball of foot pain, such as P.R.I.C.E Treatment:
- Protection: The purpose of protection is to avoid further injury to the area by protecting the injured structures. The type of protection used varies depending on the injured area but may include an ace bandage, aluminum splint, sling, protective tape, or over-the-counter brace.
- Rest: The purpose of resting is to allow the body’s own healing processes to naturally occur without being impeded by movement of the injured area. Any increase in movement of an injured tissue results in increased circulation to the area which in turn may result in further damage to the injured tissue and/or increased swelling.
- Ice: Ideally, ice packs are made of crushed ice because the crushed ice is more comfortable for the athletes and conforms to the contours of the injured area better than cubed ice. Ice can be placed into plastic or Ziploc bags. A light barrier should be placed between the skin and the ice bag (paper towel) to prevent injury to the skin during the application of the ice.
The ice pack can be secured with an ace bandage if needed. The ice should be applied for 20 minutes at a time and then removed. This can be repeated every two hours while the athlete is awake.
- Compression: When the ice pack is removed, a compression wrap should be applied to the injured area. The compression wrap serves as a mechanical barrier so that swelling is minimized in the injured area. There are a number of compression wraps available on the market, but the most commonly used is an elastic or ace bandage.
- Elevation: Elevation is important immediately post-injury to reduce the amount of blood flow to the injured area. For the lower extremities, the athlete can elevate his/her leg by lying down and elevating the injured limb on pillows. The key is that the athlete needs to have the injured area above his/her heart level.
Following the PRICE principles is an effective way to minimize the swelling in an injured area so that the athlete can return to play quickly.
Medical Interventions
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary to treat ball of foot pain effectively. Prescription medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and opioids, may be prescribed to manage ball of foot pain. Corticosteroid injections, which can be administered directly into the affected area to reduce inflammation and provide relief, may also be recommended.
Orthotics, or custom-made shoe inserts, can assist in alleviating pain and optimizing foot function. By working with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate medical interventions for your condition, you can improve your foot health and alleviate your pain.
Surgical Options
For severe or persistent ball of foot pain, surgical options may be considered. Depending on the underlying cause of the pain, surgical procedures such as:
- Metatarsal surgery
- Hammertoe repair
- Metatarsal osteotomy
- Bunion surgery
- Decompression surgery
May be recommended.
It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine if surgery is the best option for your specific condition. By exploring all available treatment options, including surgical interventions, you can develop a comprehensive plan to address your ball of foot pain and improve your quality of life.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding the anatomy of the foot, the causes of ball of foot pain, and the various treatment options available is crucial for finding relief and preventing future discomfort. By implementing preventative measures such as proper footwear, arch supports, and maintaining a healthy body weight, and seeking appropriate medical interventions when necessary, you can improve your foot health and enjoy a pain-free, active lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you relieve pain in the ball of your foot?
To relieve the pain in the ball of your foot, try at-home treatments such as ice and rest. Also, wear proper footwear with shock-absorbing insoles or arch supports to prevent future problems.
In addition, using a metatarsal pad, a surgical shoe, or a shoe insert can offload the painful part of your foot. Other helpful tips include picking shoes with good soles, a wide toe box, and a lower heel, and using soft insoles or pads.
Finally, losing weight may also help.
What does it mean when the ball of your foot is hurting?
Pain in the ball of your foot is usually caused by overuse, tight footwear or an underlying condition like arthritis. It can also be the result of a foot shape that puts extra pressure on the area, as well as hard skin or verruca.
High-impact activities such as jumping and running can be a contributing factor.
Will ball of foot pain go away on its own?
Ball of the foot pain can sometimes disappear on its own after a few days.
However, if the pain persists or is accompanied by swelling and discoloration, seek medical advice to ensure it does not worsen.
What are some common conditions that cause ball of foot pain?
Common conditions that cause ball of foot pain include metatarsalgia, Morton’s neuroma, and sesamoiditis, which are all associated with the metatarsal heads.
How can I prevent ball of foot pain?
Choose proper footwear, use arch supports and metatarsal pads, and maintain a healthy body weight to prevent ball of foot pain.
Sources and Studies
- Cook J. L. (2018). Ten treatments to avoid in patients with lower limb tendon pain. British journal of sports medicine
- . Hayes, A., Easton, K., Devanoboyina, P.T., Wu, Jian-Ping., Kirk, T.B., Lloyd, D. (2019). A review of methods to measure tendon dimensions. Journal of Orthopedic Surgery and Research. http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
- Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Foot Joints
- Metatarsalgia symptoms and causes

 of the feet, just below the toes
of the feet, just below the toes