Metatarsalgia: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Did you know that foot pain is one of the most common issues affecting millions of athletes worldwide? Metatarsalgia, a specific condition characterized by pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot, often goes unnoticed or untreated. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for metatarsalgia, as well as the importance of proper foot function and prevention strategies to keep your feet healthy and pain-free.
Short Summary
- Metatarsalgia is a painful condition affecting the metatarsal bones and heads of the foot, usually caused by inflammation or injury.
- Identifying symptoms such as pain in the ball of the foot & nerve-related issues is essential for effective treatment.
- Prevention strategies include choosing appropriate footwear, avoiding tight shoes & shoe laces, and engaging in low impact activities to maintain proper foot health.
Understanding Metatarsalgia
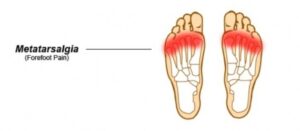 Metatarsalgia is more than just a fancy name for foot pain. It’s a condition that affects the metatarsal bones and heads located in the ball of the foot, often caused by improper footwear, foot deformities, and high-impact activities such as running or jumping.
Metatarsalgia is more than just a fancy name for foot pain. It’s a condition that affects the metatarsal bones and heads located in the ball of the foot, often caused by improper footwear, foot deformities, and high-impact activities such as running or jumping.
Proper foot function is crucial for overall health and mobility, as it provides the foundation for our posture, weight-bearing capacity, and efficient movement. Understanding the importance of metatarsalgia and its causes can help us effectively address and prevent this debilitating condition.
Ball of the Foot Pain
The primary symptom of metatarsalgia is a burning pain or shooting pain in the ball of the foot, which can be exacerbated by weight-bearing activities like walking or running. This pain is often the result of:
- inflammation or injury to the metatarsal bones and heads
- excessive pressure from ill-fitting shoes
- high arches
- certain foot shapes
In some cases, the pain may also be attributed to inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Identifying the cause of the pain is essential in finding the appropriate treatment to ease discomfort and prevent further damage.
Metatarsal Bones and Heads
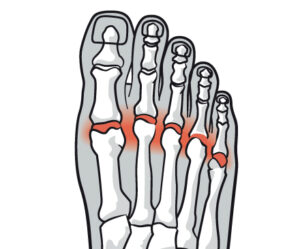 The metatarsal bones play a vital role in foot function, with the metatarsal heads acting as a bridge between the toes and ankles. These bones are responsible for various foot shapes and their functionality, with five metatarsal bones numbered from one to five, in order from the first (big toe) to the fifth toe.
The metatarsal bones play a vital role in foot function, with the metatarsal heads acting as a bridge between the toes and ankles. These bones are responsible for various foot shapes and their functionality, with five metatarsal bones numbered from one to five, in order from the first (big toe) to the fifth toe.
Factors such as foot deformities, high arches, or a longer second toe can affect the metatarsal bones and heads, leading to metatarsalgia and other foot issues. It’s important to understand the role of these bones in foot function and how they can be affected by various factors to effectively address metatarsalgia.
Importance of Proper Foot Function
Proper foot function is essential for a number of reasons. Firstly, our feet provide the foundation for our posture and weight-bearing, making them crucial for balance and stability. Secondly, the muscles within our feet are key for walking and running, aiding efficient movement and reducing the risk of injury. It’s important to pay attention to the opposite foot as well, ensuring both feet are functioning optimally.
Additionally, good foot health is vital for an active lifestyle, as our feet are complex structures with numerous bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Taking care of our feet, especially when faced with challenges like metatarsalgia, can significantly improve overall quality of life and allow us to engage in regular physical activity.
Identifying Symptoms of Metatarsalgia
Recognizing the symptoms of metatarsalgia is the first step towards getting the right treatment and relief. The primary symptom is pain in the ball of the foot, often accompanied by shooting and burning sensations that worsen during weight-bearing activities. Nerve-related issues can also contribute to metatarsalgia symptoms, making it important to seek medical advice if pain persists or worsens despite changing shoes or altering activities.
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and enable a swift return to pain-free living.
Pain in the Ball of the Foot
Pain in the ball of the foot, or metatarsalgia, can be caused by various factors. These include:
- Exercise
- Wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes
- Arthritis
- Increased pressure on the foot
- Injuries such as stress fractures
The pain is often a result of inflammation, bruising, or swelling in the metatarsal region and can be exacerbated by weight-bearing activities.
Addressing the underlying cause of the pain is essential for effective treatment and to relieve pain for long-term relief.
Shooting and Burning Sensations
Shooting and burning sensations are common symptoms of metatarsalgia and may indicate nerve-related issues. These sensations can be caused by:
- Neuropathy
- Nerve damage
- Conditions such as diabetes or burning feet syndrome
- Neurological conditions like nerve entrapment, nerve compression, or nerve inflammation
Identifying the cause of these sensations is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Nerve-related Issues
Nerve-related issues can contribute to metatarsalgia symptoms and should be addressed during diagnosis and treatment. Conditions such as tarsal tunnel syndrome, Morton’s neuroma, and peripheral neuropathy can affect the nerves in the foot, causing pain, burning, tingling, numbness, and weakness.
Physical examination and imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRIs, can help diagnose nerve-related issues and determine the most effective treatment plan to address these problems.
Causes and Risk Factors
Metatarsalgia can be caused by various factors, including improper footwear, foot deformities, and lifestyle factors. Footwear with insufficient support and high heels can put extra pressure on the ball of the foot, leading to pain and inflammation.
Foot deformities, such as high arches or a longer second toe, can also increase the risk of metatarsalgia. Furthermore, high-impact activities, such as running or jumping, can contribute to the development of this condition.
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help prevent metatarsalgia and ensure proper foot health.
Footwear and High Heels
Wearing high heels or ill-fitting shoes can contribute to the development of metatarsalgia. High heels put more pressure on the ball of the foot, increasing the risk of pain and inflammation. Ill-fitting shoes, particularly those that are too tight or narrow, can also cause discomfort and potentially lead to metatarsalgia.
To prevent foot pain and maintain proper foot function, it’s important to choose footwear that offers adequate support, cushioning, and a proper fit.
Foot Deformities and Toe Bones
Foot deformities, such as high arches or a longer second toe, can increase the risk of metatarsalgia. These deformities can cause misalignment of the toe bones, leading to increased pressure on the metatarsal bones and heads, and resulting in pain and inflammation.
Addressing these deformities through proper footwear, orthotics, or medical intervention can help alleviate metatarsalgia symptoms and improve overall foot health.
Lifestyle and Activity Factors
High-impact activities, such as running or jumping, can also contribute to the development of metatarsalgia. These high impact sports place increased stress on the feet, particularly in the ball of the foot, where metatarsalgia often occurs.
To prevent metatarsalgia and maintain proper foot health, consider engaging in low-impact activities, such as swimming or cycling, which place less stress on the feet and reduce the risk of injury.
Diagnosing Metatarsalgia
Diagnosing metatarsalgia involves:
- A physical examination of the foot to assess the severity of metatarsalgia and identify any underlying issues
- Imaging tests to get a clearer picture of the foot’s structure and identify any abnormalities
- Ruling out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms
A thorough physical examination is necessary to accurately diagnose metatarsalgia and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs, can help determine the cause of the pain, while ruling out other conditions, such as arthritis or gout, is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination of the foot is necessary to diagnose metatarsalgia and assess its severity. During the examination, your doctor will:
- Inquire about your symptoms and medical history
- Conduct a visual inspection of your foot to identify any signs of injury or deformity
- Apply pressure to various areas of the foot to evaluate tenderness or discomfort
This comprehensive examination helps your doctor determine the root cause of your pain and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs, can help identify underlying issues contributing to metatarsalgia. These tests can detect bone spurs, stress fractures, or other structural abnormalities that could be causing your pain.
In some cases, more advanced imaging techniques, such as bone scans, may be necessary to identify areas of inflammation and help your doctor differentiate metatarsalgia from other conditions with similar symptoms.
Ruling Out Other Conditions
Ruling out other conditions, such as arthritis or gout, is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. While metatarsalgia shares some symptoms with these conditions, the underlying causes and treatments may differ.
Your doctor will consider your medical history, physical examination, and imaging test results to rule out other potential causes of your foot pain and develop a targeted treatment plan for your specific case of metatarsalgia.
Get a Virtual Sports Specialized appointment within 5 minutes for $29
 When you have questions like: I have an injury and how should I manage it? How severe is it and should I get medical care from an urgent care center or hospital? Who can I talk to right now? SportsMD Virtual Urgent Care is available by phone or video anytime, anywhere 24/7/365, and appointments are within 5 minutes. Learn more via SportsMD’s Virtual Urgent Care Service.
When you have questions like: I have an injury and how should I manage it? How severe is it and should I get medical care from an urgent care center or hospital? Who can I talk to right now? SportsMD Virtual Urgent Care is available by phone or video anytime, anywhere 24/7/365, and appointments are within 5 minutes. Learn more via SportsMD’s Virtual Urgent Care Service.
Treatment Options for Metatarsalgia
Treatment options for metatarsalgia include footwear and orthotic solutions, lifestyle changes, and medical interventions. Depending on the severity and underlying cause of your pain, your doctor may recommend a combination of these approaches to effectively alleviate your symptoms and prevent future complications.
By addressing the root cause of your metatarsalgia and implementing appropriate treatment strategies, you can regain your mobility and enjoy a pain-free life.
Footwear and Orthotic Solutions
Proper footwear and orthotic devices, such as metatarsal pads or shoe inserts, can help alleviate metatarsalgia symptoms. Supportive and well-fitting shoes can distribute pressure evenly across the foot, reducing stress on the metatarsal bones and heads.
Metatarsal pads or shoe inserts can provide additional cushioning and support to the ball of the foot, further relieving pressure and discomfort. Your doctor or a qualified professional, such as a physical therapist, can help you select the most appropriate footwear and orthotic solutions for your specific needs.
Lifestyle Changes and Weight Management
Lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and engaging in low-impact activities, can help prevent and treat metatarsalgia. Excess weight can put additional pressure on your feet, increasing the risk of metatarsalgia and other foot-related issues.
By maintaining a healthy weight and participating in low-impact activities like swimming or cycling, you can reduce stress on your feet and minimize your risk of developing metatarsalgia.
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions, such as injections or surgery, may be necessary for severe cases of metatarsalgia or when conservative treatments fail. Injections, such as corticosteroids or local anesthetics, can help alleviate pain and inflammation in the affected area.
Surgical intervention may be necessary to correct foot deformities, such as hammertoes or bunions, or to relieve pressure on a trapped or irritated nerve. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate medical intervention for your specific case based on the underlying cause of your metatarsalgia and the severity of your symptoms.
Prevention Strategies
Prevention strategies for metatarsalgia include choosing the right footwear, avoiding tight shoes and high heels, and engaging in low-impact activities. Selecting supportive and well-fitting shoes can help distribute body weight evenly across the foot, reducing the risk of metatarsalgia.
Avoiding tight shoes and high heels can further protect your feet from excessive pressure and strain. Lastly, engaging in low-impact activities can help maintain foot health and prevent metatarsalgia from developing in the first place.
Choosing the Right Footwear
Selecting the right footwear is crucial for preventing metatarsalgia and maintaining proper foot function. Here are some features to look for in shoes to help reduce the risk of metatarsalgia:
- Cushioning and support in the ball of the foot
- High, broad toe box
- Rocker sole
- Metatarsal pads
- Good arch support
Selecting the correct shoes and replacing them periodically can help to avoid direct  pressure on extensor tendons and prevent recurrence of metatarsalgia. Shoes that provide good arch support, are flexible, lightweight, and of the right width are recommended for preventing and treating metatarsalgia. In particular, the Women’s Fresh Foam X 1080v12, Men’s Fresh Foam X 880v13 or the Mizuno Wave Inspire 14 Running Shoes can be considered for their cushioning, support, and shock absorption.
pressure on extensor tendons and prevent recurrence of metatarsalgia. Shoes that provide good arch support, are flexible, lightweight, and of the right width are recommended for preventing and treating metatarsalgia. In particular, the Women’s Fresh Foam X 1080v12, Men’s Fresh Foam X 880v13 or the Mizuno Wave Inspire 14 Running Shoes can be considered for their cushioning, support, and shock absorption.
The The v12 and v13 offers a supportive, second-skin style fit with an engineered Hypoknit upper which may releive pressure on the extensor tendons.
Taking the time to choose the right athletic shoes can make a significant difference in your foot health and overall well-being.
Avoiding Tight Shoes and High Heels
Avoiding to wear tight shoes and high heels can significantly reduce your risk of developing metatarsalgia. Tight shoes can cause undue pressure on the metatarsal bones and heads, leading to inflammation and pain. High heels, on the other hand, shift your body weight forward, increasing pressure on the ball of your foot and potentially leading to metatarsalgia.
Opting for comfortable, well-fitting shoes with adequate support and cushioning can help prevent metatarsalgia and ensure proper foot health.
Engaging in Low-Impact Activities
Incorporating low-impact activities into your daily routine can help maintain foot health and prevent metatarsalgia. Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling place less stress on your feet and reduce the risk of injury due to exercise.
By engaging in a variety of low-impact activities, you can keep your feet healthy, strengthen your muscles and joints, and minimize the risk of developing metatarsalgia.
Summary
In conclusion, metatarsalgia is a common but often overlooked cause of foot pain that can significantly impact your daily life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition. Choosing the right footwear, avoiding tight shoes and high heels, and engaging in low-impact activities are all effective strategies for maintaining proper foot function and preventing metatarsalgia. Remember, taking care of your feet is an investment in your overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the fastest way to cure metatarsalgia?
The fastest way to cure metatarsalgia is to rest, protect your foot from further injury, apply ice packs several times a day, take OTC pain medication, wear proper shoes and use metatarsal pads and arch supports.
These treatments can help reduce inflammation and pain, and help you get back to your normal activities. It is important to note that metatarsalgia can take several weeks to heal, so it is important to be patient and follow your doctor’s instructions.
What does metatarsalgia feel like?
Metatarsalgia can feel like a sharp or shooting pain, numbness, tingling in the toes, or having a pebble in your shoe. It can also cause aching, burning pain in the ball of your foot that worsens when standing, running, flexing your feet, or walking barefoot on hard surfaces, but improves when resting.
Metatarsalgia is a common foot condition that can cause pain and discomfort in the ball of your foot. It is often caused by overuse, injury, or wearing ill-fitting shoes. Treatment options include rest, ice, stretching, orthotics, and ice.
Does metatarsalgia go away?
Metatarsalgia usually resolves on its own within several days, but if it persists or worsens, prompt management may be necessary for complete recovery in 6 to 8 weeks.
How do you overcome metatarsalgia?
To overcome metatarsalgia, it is important to rest the foot and use ice compresses to reduce pain and swelling. Over-the-counter pain medications can also provide relief.
Wearing the correct shoes with arch supports and metatarsal pads can help alleviate pressure off the affected area.
Why does the bottom of my foot hurt by my toes?
Pain in the bottom of your foot by your toes is often caused by exercise, wearing shoes that are too tight or a medical condition such as plantar fasciitis.
Additionally, foot shape and hard or cracked skin can also cause this type of pain.
Sources and Studies
- Cook J. L. (2018). Ten treatments to avoid in patients with lower limb tendon pain. British journal of sports medicine
- . Hayes, A., Easton, K., Devanoboyina, P.T., Wu, Jian-Ping., Kirk, T.B., Lloyd, D. (2019). A review of methods to measure tendon dimensions. Journal of Orthopedic Surgery and Research. http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
- Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Foot Joints
- Metatarsalgia symptoms and causes

